YugabyteDB Kubernetes Operator
The YugabyteDB Kubernetes Operator streamlines the deployment and management of YugabyteDB clusters in Kubernetes environments. You can use the Operator to automate provisioning, scaling, and handling lifecycle events of YugabyteDB clusters, and it provides additional capabilities not available via other automation methods (which rely on REST APIs, UIs, and Helm charts).
The Operator establishes ybuniverse as a Custom Resource (CR) in Kubernetes, and enables a declarative management of your YugabyteDB Anywhere (YBA) universe. You can update the custom resources to customize the ybuniverse resources, including CPU, memory, and disk configurations, and deploy multi-availability zone balanced YBA universes on the underlying cluster for optimal performance. The CR supports seamless upgrades of YBA universes with no downtime, as well as transparent scaling operations.
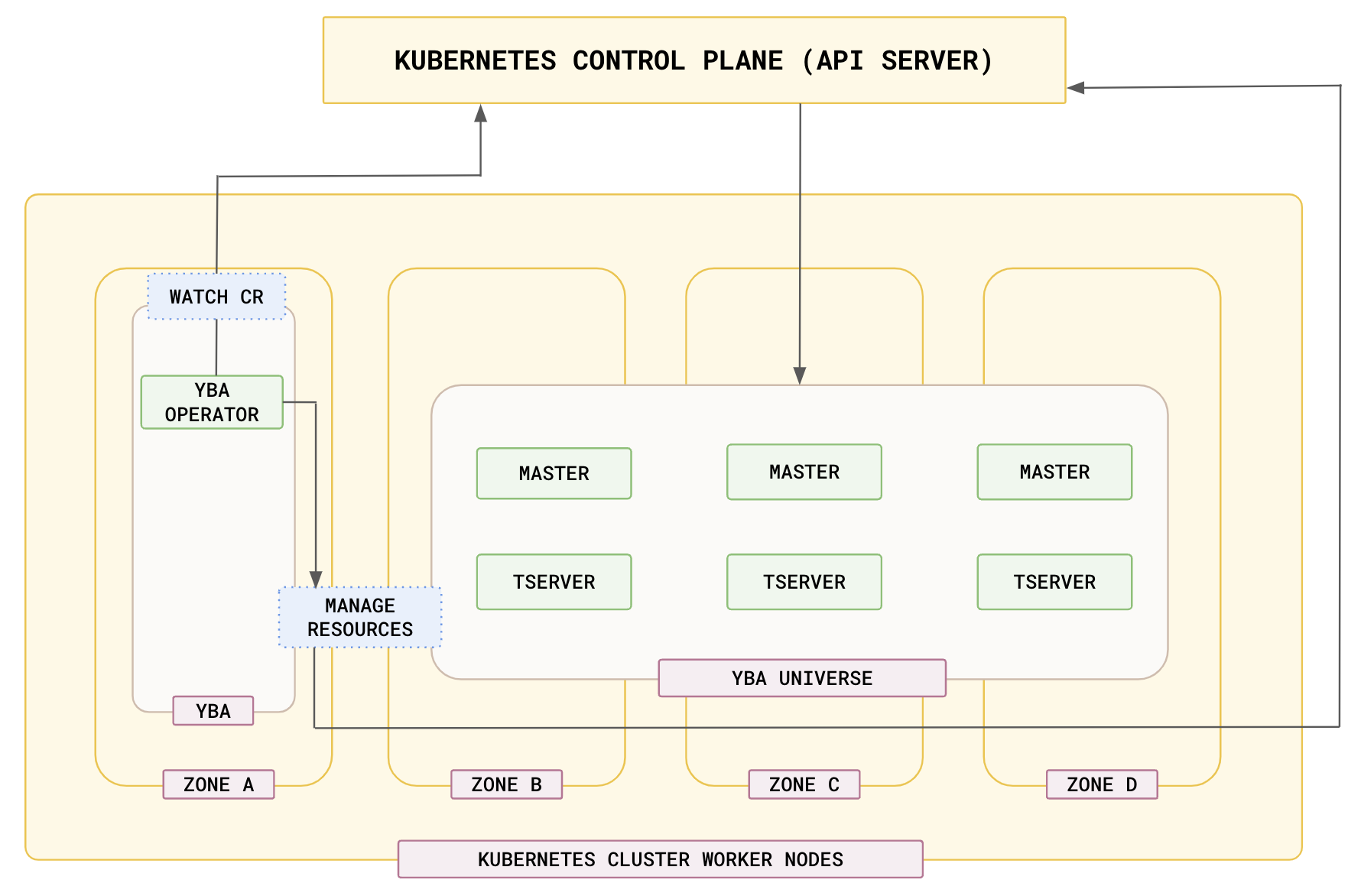
YugabyteDB Kubernetes Operator CRDs
The YugabyteDB Operator provides additional Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs) to manage the day 2 operations of a YBA universe, including the following:
- Release CRD - run multiple releases of YugabyteDB and upgrade the software in a YBA universe
- Support Bundle CRD - collect logs when a universe fails
- Backup and Restore CRDs - take full backups of a universe and restore for data protection
- Storage Config CRD - configure backup destinations
For details of each CRD, you can run a kubectl explain on the CR. For example:
kubectl explain ybuniverse.spec
GROUP: operator.yugabyte.io
KIND: YBUniverse
VERSION: v1alpha1
FIELD: spec <Object>
DESCRIPTION:
Schema spec for a yugabytedb universe.
FIELDS:
deviceInfo <Object>
Device information for the universe to refer to storage information for
volume, storage classes etc.
enableClientToNodeEncrypt <boolean>
Enable client to node encryption in the universe. Enable this to use tls
enabled connnection between client and database.
enableIPV6 <boolean>
Enable IPV6 in the universe.
enableLoadBalancer <boolean>
Enable LoadBalancer access to the universe. Creates a service with
Type:LoadBalancer in the universe for tserver and masters.
enableNodeToNodeEncrypt <boolean>
Enable node to node encryption in the universe. This encrypts the data in
transit between nodes.
enableYCQL <boolean>
Enable YCQL interface in the universe.
enableYCQLAuth <boolean>
enableYCQLAuth enables authentication for YCQL inteface.
enableYSQL <boolean>
Enable YSQL interface in the universe.
enableYSQLAuth <boolean>
enableYSQLAuth enables authentication for YSQL inteface.
gFlags <Object>
Configuration flags for the universe. These can be set on masters or
tservers
kubernetesOverrides <Object>
Kubernetes overrides for the universe. Please refer to yugabyteDB
documentation for more details.
https://docs.yugabyte.com/stable/yugabyte-platform/create-deployments/create-universe-multi-zone-kubernetes/#helm-overrides
numNodes <integer>
Number of tservers in the universe to create.
providerName <string>
Preexisting Provider name to use in the universe.
replicationFactor <integer>
Number of times to replicate data in a universe.
universeName <string>
Name of the universe object to create
ybSoftwareVersion <string>
Version of DB software to use in the universe.
ycqlPassword <Object>
Used to refer to secrets if enableYCQLAuth is set.
ysqlPassword <Object>
Used to refer to secrets if enableYSQLAuth is set.
zoneFilter <[]string>
Only deploy yugabytedb nodes in these zones mentioned in the list. Defaults
to all zones if unspecified.
kubectl explain ybuniverse.spec.gFlags
GROUP: operator.yugabyte.io
KIND: YBUniverse
VERSION: v1alpha1
FIELD: gFlags <Object>
DESCRIPTION:
Configuration flags for the universe. These can be set on masters or
tservers
FIELDS:
masterGFlags <map[string]string>
Configuration flags for the master process in the universe.
perAZ <map[string]Object>
Configuration flags per AZ per process in the universe.
tserverGFlags <map[string]string>
Configuration flags for the tserver process in the universe.
Prerequisites
Before installing the Kubernetes Operator and YBA universes, verify that the following components are installed and configured:
- Kubernetes cluster v1.27 or later.
- Helm v3.11 or later.
- Administrative access. Required for the Kubernetes cluster, including ability to create cluster roles, namespaces, and details on setting up necessary roles and permissions for the service account.
Service account
The YugabyteDB Kubernetes Operator requires a service account with sufficient permissions to manage resources in the Kubernetes cluster. When installing the operator, ensure that the service account has the necessary roles and cluster roles bound to it.
Cluster roles and namespace roles
ClusterRole: grants permissions at the cluster level, necessary for operations that span multiple namespaces, or have cluster-wide implications.Role: grants permissions in a specific namespace, and used for namespace-specific operations.
The yugaware chart, when installed with rbac.create=true, automatically creates appropriate ClusterRoles and Roles needed for the Kubernetes Operator.
Installation
For information on installing YBA and creating universes using the YugabyteDB Kubernetes Operator, refer to Use YugabyteDB Kubernetes Operator to automate YBA deployments.
Example workflows
Create a universe
Use the following CRD to create a universe using the kubectl apply command:
kubectl apply universedemo.yaml -n yb-platform
# universedemo.yaml
apiVersion: operator.yugabyte.io/v1alpha1
kind: YBUniverse
metadata:
name: operator-universe-demo
spec:
numNodes: 3
replicationFactor: 1
enableYSQL: true
enableNodeToNodeEncrypt: true
enableClientToNodeEncrypt: true
enableLoadBalancer: false
ybSoftwareVersion: "2.20.1.3-b3"
enableYSQLAuth: false
enableYCQL: true
enableYCQLAuth: false
gFlags:
tserverGFlags: {}
masterGFlags: {}
deviceInfo:
volumeSize: 400
numVolumes: 1
storageClass: "yb-standard"
kubernetesOverrides:
resource:
master:
requests:
cpu: 2
memory: 8Gi
limits:
cpu: 3
memory: 8Gi
Any modifications to the universe can be done by modifying the CRD using kubectl apply/edit operations.
Add a different software release of YugabyteDB
Use the release CRD to add a different software release of YugabyteDB:
kubectl apply updaterelease.yaml -n yb-platform
# updaterelease.yaml
apiVersion: operator.yugabyte.io/v1alpha1
kind: Release
metadata:
name: "2.20.1.3-b3"
spec:
config:
version: "2.20.1.3-b3"
downloadConfig:
http:
paths:
helmChart: "https://charts.yugabyte.com/yugabyte-2.20.1.tgz"
x86_64: "https://software.yugabyte.com/releases/2.20.1.3/yugabyte-2.20.1.3-b3-linux-x86_64.tar.gz"
Backup and restore
Specify a storage configuration CRD to configure backup storage, and perform backup and restore of your YBA universes as per the following example:
kubectl apply backuprestore.yaml -n yb-platform
# backuprestore.yaml
apiVersion: operator.yugabyte.io/v1alpha1
kind: StorageConfig
metadata:
name: s3-config-operator
spec:
config_type: STORAGE_S3
data:
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID: <ACCESS_KEY>
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY: <SECRET>
BACKUP_LOCATION: s3://backups.yugabyte.com/s3Backup
apiVersion: operator.yugabyte.io/v1alpha1
kind: Backup
metadata:
name: operator-backup-1
spec:
backupType: PGSQL_TABLE_TYPE
storageConfig: s3-config-operator
universe: <name-universe>
timeBeforeDelete: 1234567890
keyspace: postgres
apiVersion: operator.yugabyte.io/v1alpha1
kind: RestoreJob
metadata:
name: operator-restore-1
spec:
actionType: RESTORE
universe: <name of universe>
backup: <name of backup to restore>
keyspace: <keyspace overide>
Service account for backup
You can attach a service account to database pods to be used to access storage in S3 or GCS. The service account used for the database pods should have annotations for the IAM role. The service account to be used can be applied to the database pods as a Helm override with provider- or universe- level overrides.
The operator pod (with the YugabyteDB Anywhere instance) should have the IAM role for cloud storage access attached to its service account.
AWS
The IAM role used should be sufficient to access storage in S3.
To enable IAM roles to access storage in S3, set the Use S3 IAM roles attached to DB node for Backup/Restore Universe Configuration option (config key yb.backup.s3.use_db_nodes_iam_role_for_backup) to true. Refer to Manage runtime configuration settings.
The storage config CR should have IAM as the credential source.
apiVersion: operator.yugabyte.io/v1alpha1
kind: StorageConfig
metadata:
name: s3-config-operator
spec:
config_type: STORAGE_S3
data:
BACKUP_LOCATION: s3://backups.yugabyte.com/test
USE_IAM: true //For IAM based access on GCP/S3
Provide the service account in the universe overrides section. The service account should have IAM roles configured for access to cloud storage.
apiVersion: operator.yugabyte.io/v1alpha1
kind: YBUniverse
metadata:
name: operator-universe
spec:
...
kubernetesOverrides:
tserver:
serviceAccount: <KSA_NAME>
For more information, refer to Enable IAM roles for service accounts in the AWS documentation.
GKE
The IAM role used should be sufficient to access storage in GCS.
The storage config CR should have IAM as the credential source.
apiVersion: operator.yugabyte.io/v1alpha1
kind: StorageConfig
metadata:
name: gcs-config-operator
spec:
config_type: STORAGE_GCS
data:
BACKUP_LOCATION: gs://gcp-bucket/test_backups
USE_IAM: true //For IAM based access on GCP/S3
Provide the service account in the universe overrides section. The service account should have IAM roles configured for access to cloud storage.
apiVersion: operator.yugabyte.io/v1alpha1
kind: YBUniverse
metadata:
name: operator-universe
spec:
...
kubernetesOverrides:
tserver:
serviceAccount: <KSA_NAME>
For more information, refer to Authenticate to Google Cloud APIs from GKE workloads in the Google Cloud documentation.
Scheduled backups
This feature is EA . Backup schedules support taking full backups based on cron expressions or specified frequencies. They also allow you to configure incremental backups to run in between these full backups, providing finer-grained recovery points.
When an operator schedule triggers a backup, a corresponding CR is automatically created for that specific backup. The operator names this CR appropriately, and marks it with "ignore-reconciler-add".
Operator schedules maintain owner references to their respective YugabyteDB Anywhere universes. This ensures that when you delete a source universe, its associated schedule is also deleted.
The operator's backup schedule also supports Point-In-Time Recovery (PITR) from a backup. See Create a scheduled backup policy with PITR for more details.
Setup
Set up scheduled backups as follows:
-
Apply latest CRDs with new scheduled backups CRD on the Kubernetes cluster.
kubectl apply -f https://raw.github.com/yugabyte/charts/2025.1.1/crds/concatenated_crd.yaml -
Verify scheduled backup fields in the backup CRD specification using
kubectl explainto understand the available configuration options.$ kubectl explain backupschedules.operator.yugabyte.io.specGROUP:operator.yugabyte.io KIND:BackupSchedule VERSION:v1alpha1 FIELDS: backupType<string>-required- Type of backup to be taken. Allowed values are - YQL_TABLE_TYPE PGSQL_TABLE_TYPE cronExpression<string> Frequency of full backups in cron expression. enablePointInTimeRestore<boolean> Enable Point in time restore for backups created with the schedule incrementalBackupFrequency<integer> Frequency of incremental backups in milliseconds keyspace<string>-required- Name of keyspace to be backed up. schedulingFrequency<integer> Frequency of full backups in milliseconds. storageConfig<string>-required- Storage configuration for the backup, refers to a storageconfig CR name. Should be in the same namespace as the backupschedule. tableByTableBackup<boolean> Boolean indicating if backup is to be taken table by table. timeBeforeDelete<integer> Time before backup is deleted from storage in milliseconds. universe<string>-required- Name of the universe for which backup is to be taken, refers to a ybuniverse CR name. Should be in the same namespace as the backupschedule.
Example
This example decribes how to create and delete scheduled backups, and assumes you have the following:
- An existing YugabyteDB Anywhwere universe deployed using the YugabyteDB Kubernetes Operator.
- A configured storage location for your backups.
Use the following CRD to create a scheduled backup:
kubectl apply scheduled-backup-demo.yaml -n schedule-cr
apiVersion:operator.yugabyte.io/v1alpha1
kind:BackupSchedule
metadata:
name:operator-scheduled-backup-1
spec:
backupType:PGSQL_TABLE_TYPE
storageConfig:s3-config-operator
universe:operator-universe-test-2
timeBeforeDelete:1234567890
keyspace:test
schedulingFrequency:3600000
incrementalBackupFrequency:900000
Backups are created from the schedules (using their auto-created CRs). You can verify them using the kubectl get backups as follows:
kubectl get backups -n schedule-cr
NAME AGE
operator-scheduled-backup-1-1069296176-full--06-43-25 32m
operator-scheduled-backup-1-1069296176-incremental--06-59-26 16m
operator-scheduled-backup-1-1069296176-incremental--07-13-26 2m55s
Backup schedules get automatically deleted when you delete the YBA universe that owns it as per the following:
$kubectl get backups -n schedule-cr
NAME AGE
operator-scheduled-backup-1 101m
$ kubectl get ybuniverse -n schedule-cr
NAME STATE SOFTWARE VERSION
operator-universe-test-2 Ready 2.25.2.0-b40
# Delete YBA universe
$ kubectl delete ybuniverse operator-universe-test-2 -n schedule-cr
ybuniverse.operator.yugabyte.io "operator-universe-test-2" deleted
$ kubectl get backupschedule -n schedule-cr
No resources found in schedule-cr namespace.
Incremental backups
EA Use backup schedules to schedule full backups at specific intervals or using a cron expression. You can also configure incremental backups to run in between these full backups, providing finer-grained recovery points.
This functionality creates a chain of references for your backups. Each incremental backup CR references its preceding backup in the chain, whether a full or another incremental backup. This chain always leads back to the initial full backup.
When you initiate an incremental backup, it is appended to the last successful backup (either full or incremental) within that existing chain. This ensures a consistent and complete backup history.
To delete the backups, you delete the first full backup, and this action triggers a chain of deletes. You cannot delete individual incremental backups, as doing so can break the backup chain.
Setup
Set up incremental backups as follows:
-
Apply the latest CRD for backup:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.github.com/yugabyte/charts/2025.1.1/crds/concatenated_crd.yaml -
Verify incremental backup fields in the backup CRD specification using
kubectl explainto understand the available configuration options.$ kubectl explain backups.operator.yugabyte.io.specGROUP: operator.yugabyte.io KIND: Backup VERSION: v1alpha1 FIELDS: ... incrementalBackupBase <string> Base backup Custom Resource name. Operator will add an incremental backup to the existing chain of backups at the last.
Example
This example decribes how to create and delete incremental backups, and assumes you have the following:
- An existing YugabyteDB Anywhwere universe deployed using the YugabyteDB Kubernetes Operator.
- A configured storage location for your backups. You must have an existing base backup (either a full backup or a previous incremental backup) to create the new incremental backup.
Use the following CRD to create an incremental backup:
kubectl apply operator-backup-demo.yaml -n schedule-cr
#operator-backup-demo.yaml
apiVersion: operator.yugabyte.io/v1alpha1
kind: Backup
metadata:
name: operator-backup-1
spec:
backupType: PGSQL_TABLE_TYPE
storageConfig: az-config-operator-1
universe: operator-universe-test-1
timeBeforeDelete: 1234567890
keyspace: test
incrementalBackupBase: <base full backup cr name>
Deleting full backup deletes all incremental backups associated with it as follows:
# Get all backups in the 'schedule-cr' namespace.
$ kubectl get backups -n schedule-cr
NAME AGE
operator-scheduled-backup-1-1069296176-full-2025-02-27-06-43-25 32m
operator-scheduled-backup-1-1069296176-incremental-2025-02-27-06-59-26 16m
operator-scheduled-backup-1-1069296176-incremental-2025-02-27-07-13-26 2m55s
$ kubectl delete backup operator-scheduled-backup-1-1069296176-full-2025-02-27-06-43-25 -n schedule-cr
$ kubectl get backups -n schedule-cr
No resources found in schedule-cr namespace.
Support bundle
Use the following CRD to create a support bundle:
kubectl apply supportbundle.yaml -n yb-platform
# supportbundle.yaml
apiVersion: operator.yugabyte.io/v1alpha1
kind: SupportBundle
metadata:
name: bundle1
namespace: user-test
spec:
universeName: test-1
collectionTimerange:
startDate: 2023-08-07T11:55:00Z
components:
- UniverseLogs
- ApplicationLogs
- OutputFiles
- ErrorFiles
- CoreFiles
- Instance
- ConsensusMeta
- TabletMeta
- YbcLogs
- K8sInfo
- GFlags
Limitations
- YugabyteDB Kubernetes Operator can only deploy universes on the same Kubernetes cluster it is deployed on.
- YugabyteDB Kubernetes Operator is single cluster only, and does not support multi-cluster universes.
- Currently, YugabyteDB Kubernetes Operator does not support the following features:
- Software upgrade rollback
- xCluster
- Read Replica
- Encryption-At-Rest
- Only self-signed encryption in transit is supported. Editing this later is not supported.